Schematic Diagram of Pig Slaughter
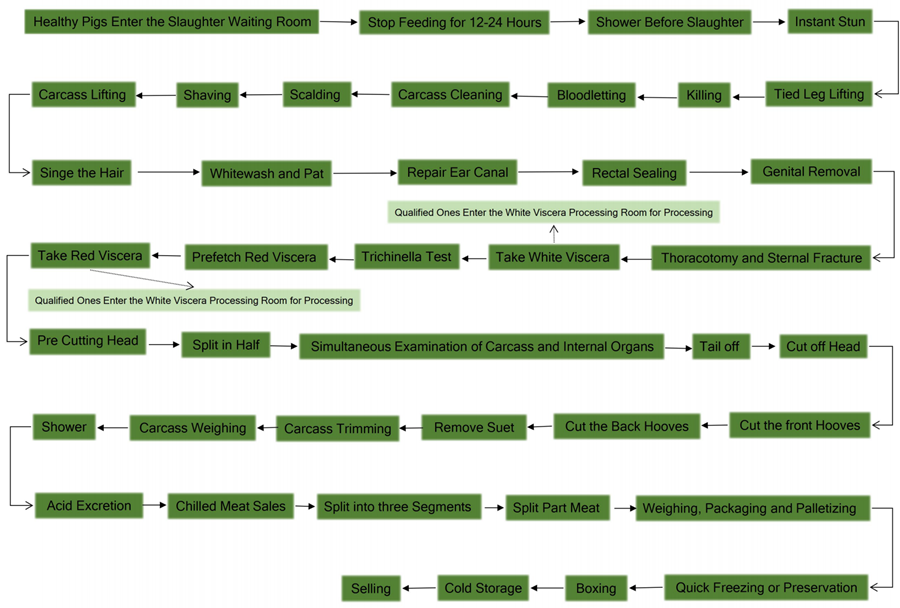
Pig Slaughter Process:
Step 1: Slaughter Waiting Room Management
1.1. Once trucks arrive at the processing plant, please observe all sheep before unloading. If no abnormality is found, then ask for the certificate of conformity, which is issued by the animal epidemic prevention supervision agency of the place of origin. Only when the certificate matches the goods, the trucks are allowed to be unloaded.
1.2. After unloading the truck, the quarantine personnel must observe the health status of the live pigs one by one, divide and number them according to the inspection results. Qualified and healthy pigs are rushed into the slaughter waiting room to rest; Suspiciously sick ones are rushed into the quarantine pen and continue to observe; Sick pigs and disabled pigs are sent to the emergency slaughter room for treatment.
1.3. For suspicious pigs, after drinking water and adequate rest, those who return to normal can be rushed into the slaughter waiting room; If the symptoms are still not alleviated, send them to the emergency slaughter room for treatment.
1.4. The pigs should be stopped eating and rest for 24 hours before being sent to slaughter. In order to eliminate fatigue during transportation and restore a normal physiological state. During the rest period, the quarantine staff will observe regularly and send the suspicious pigs to the isolation stall for observation. Once found the confirmed sick ones, will send to the emergency slaughter room for treatment. The healthy and qualified pigs will be stopped drinking water 3 hours before slaughter.
1.5. The pigs should be showered before entering the slaughterhouse, to wash off the dirt and microorganisms on the body, and it is also convenient to stun. When showering, control the water pressure and don’t be too rushed to avoid excessive stress on the pigs.
1.6. After the shower, the pigs are driven into the slaughterhouse through the pig road. The pig-driving road is generally designed as an “八” type. In the beginning, the pig-driving road can accommodate 2-4 pigs side by side, and gradually only one pig can go forward, and the pig body cannot turn around and go back. At this time, the width of the pig-driving lane is designed to be no more than 450mm.
Step 2: Pig Instant Stunning
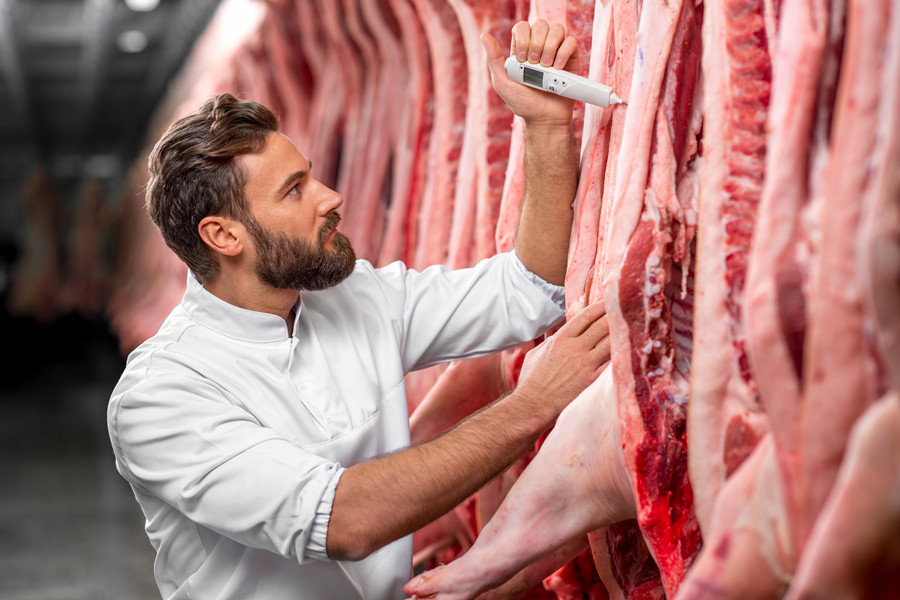
2.1. Stunning is an important part of the pig slaughter process. The purpose of using instant stunning is to temporarily lose consciousness and be in a coma to assassinate and bleed, ensure the safety of assassination operators, reduce labor intensity, improve labor productivity, keep the environment around the slaughterhouse quiet, and improve meat at the same time. The quality of the product.

Step 3: Killing and Bloodletting
3.1. Horizontal Bloodletting: The stunned pig slides into the horizontal bloodletting flat conveyor through the chute, and the bloodletting is stabbed with a knife. After 1-2 minutes of blood draining, 90% of the blood flows into the blood collection tank. This slaughter method is conducive to the collection and utilization of blood and also improves the slaughter capacity. It is also the perfect combination with the three-point electric stunner.
3.2. Handstand Bloodletting: The stunned pig is tied to a back leg with a buckle chain, and lifted into the track of the automatic bloodletting line by a hoist or the lifting device of the bloodletting line, and then and then assassinated with a knife.

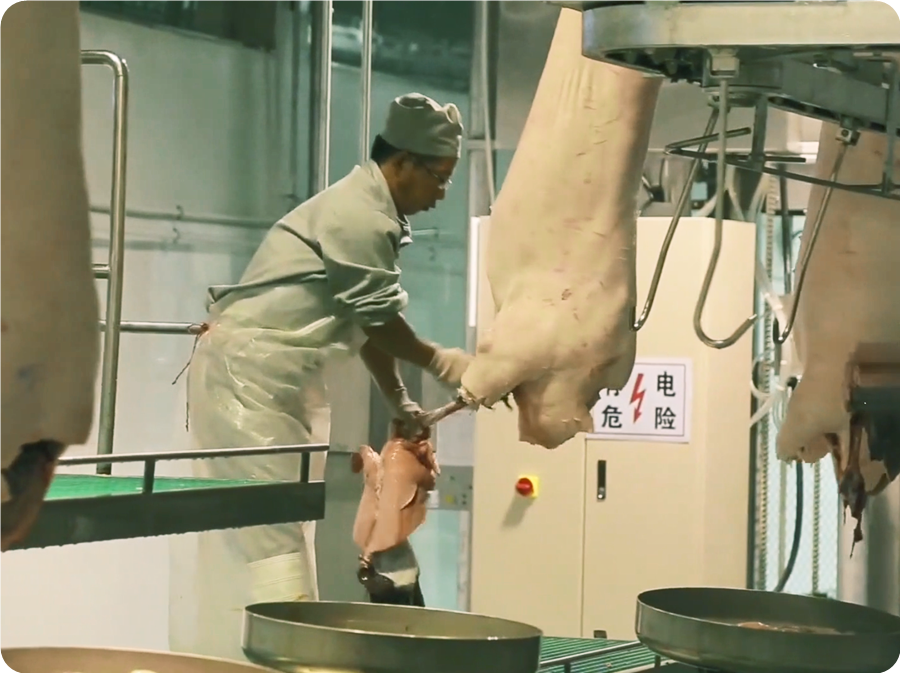
Step 4: Scalding and Shaving
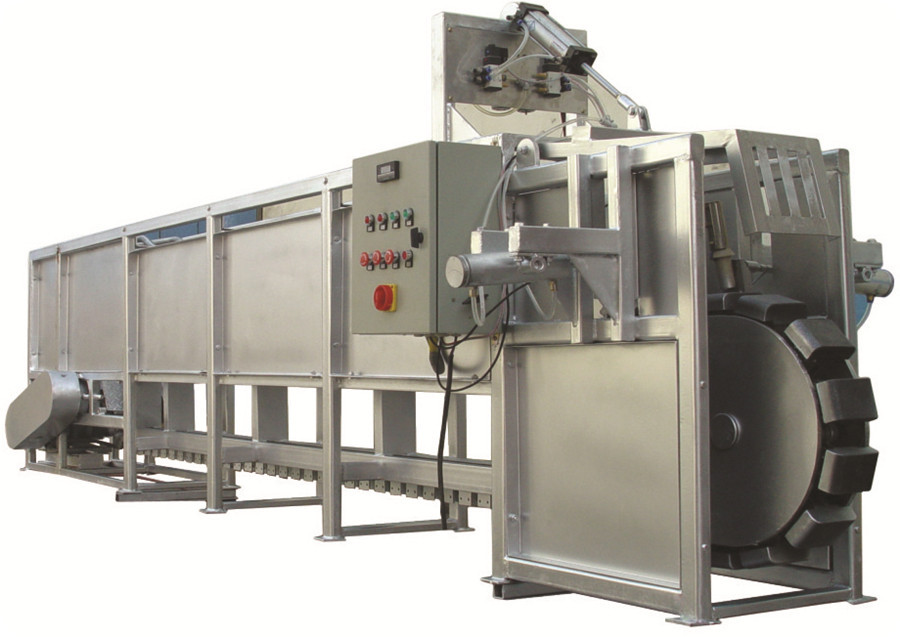
4.1. Scalding in the Pig Pool: Unloading the blooded pigs into the receiving table of the scalding pool through the pig unloading device, and slowly slide the body into the scalding pool for scalding. There are manual blanching methods and pig blanching machine shaking blanching methods. The water temperature is generally controlled between 58-62℃. If it is too high, it will scald the pig’s body white and affect the hair removal effect. Soaking time: 4-6minutes. A “skylight” is designed directly above the pig scalding pool to discharge water vapor.
4.2. Enclosed Canal-type Pig Scalding Pool for Scalding: The blood-exhausted pigs are automatically transported by the bloodletting automatic conveying line through the downward curved rail into the canal-type pig scalding pool and immersed in the enclosed pig scalding pool for 4-6 minutes. During the process, the pressure rod should press the pig body to prevent floating. The scalded pigs are automatically conveyed by the automatic conveying line through the uphill curved rail. This kind of hot pig pool has a good heat preservation effect

4.3. Tunnel Type Steam Scalding System: Hang the pig on the automatic blood-letting conveyor line to enter the tunnel to scald. This method greatly reduces the labor intensity of workers, improves work efficiency, and realizes mechanized operation. At the same time, the disadvantages of cross-infection between pigs are avoided, and the meat quality is more hygienic. This is currently the most advanced and ideal form of scalding.
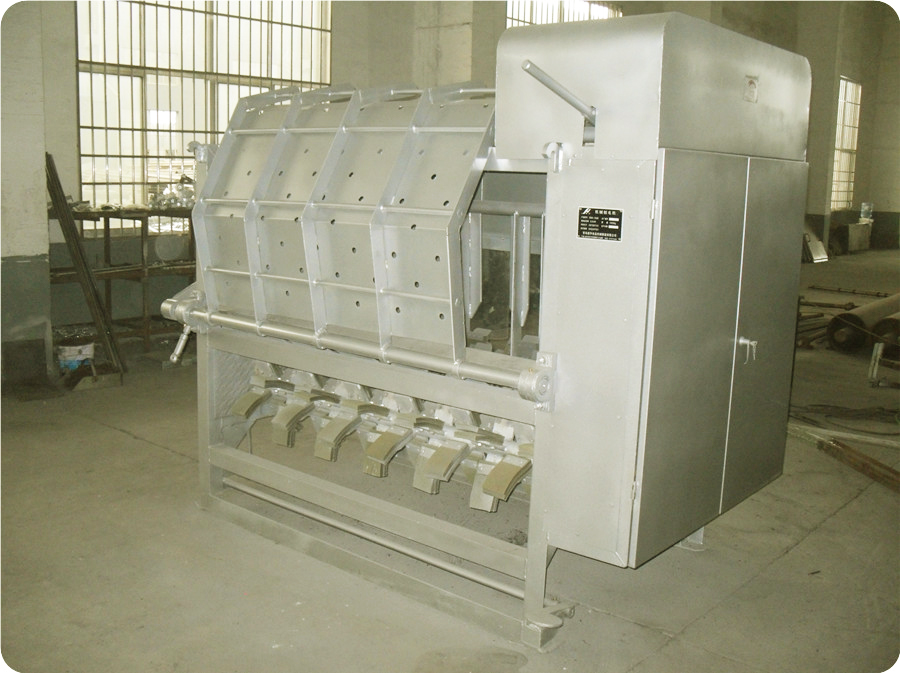
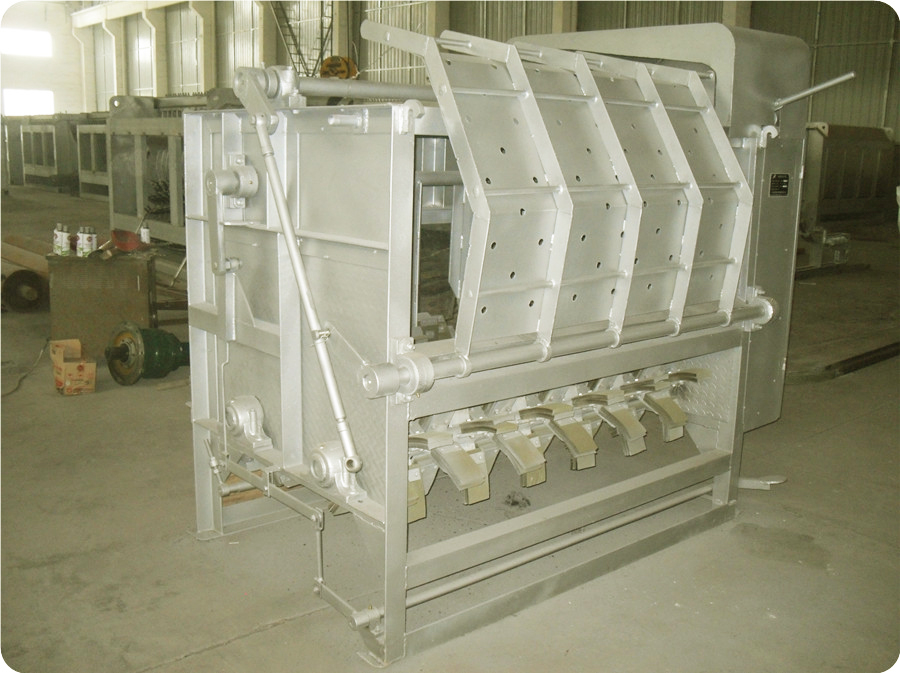
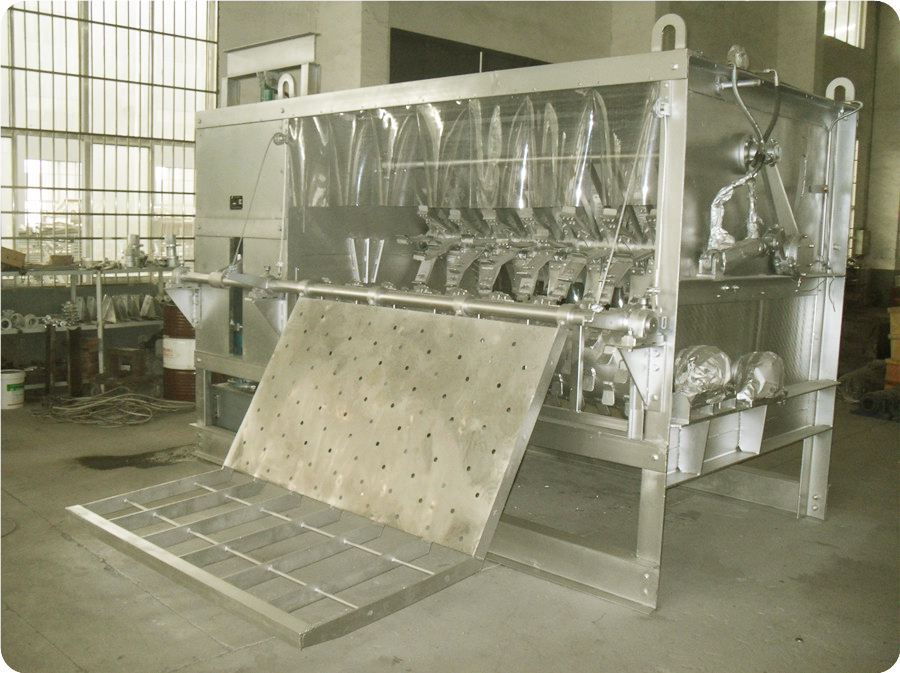
4.4. Horizontal Shaved: This method adopts 100-type, 200-type mechanical (hydraulic), and 300-type mechanical (hydraulic) shaving machines. The scalded pig is taken out of the scalding pool with a rake and automatically enters the shaver. The pig’s hair is shaved by the tumbling of the big drum and the soft shaved claws, and then they are released into the shave conveyor or clean water tank for scraping.
4.5. Spiral Automatic Shaved: It is used together with canal-style scalding and tunnel-type steam scalding. The scalded pigs are unloaded from the bloodletting automatic conveyor line into the shaving machine, then pushed out from the other end of the shaver through the soft planing claw shaving and spiral propulsion, and enters the shaved conveyor for scraping.

Step 5: Carcass Processing
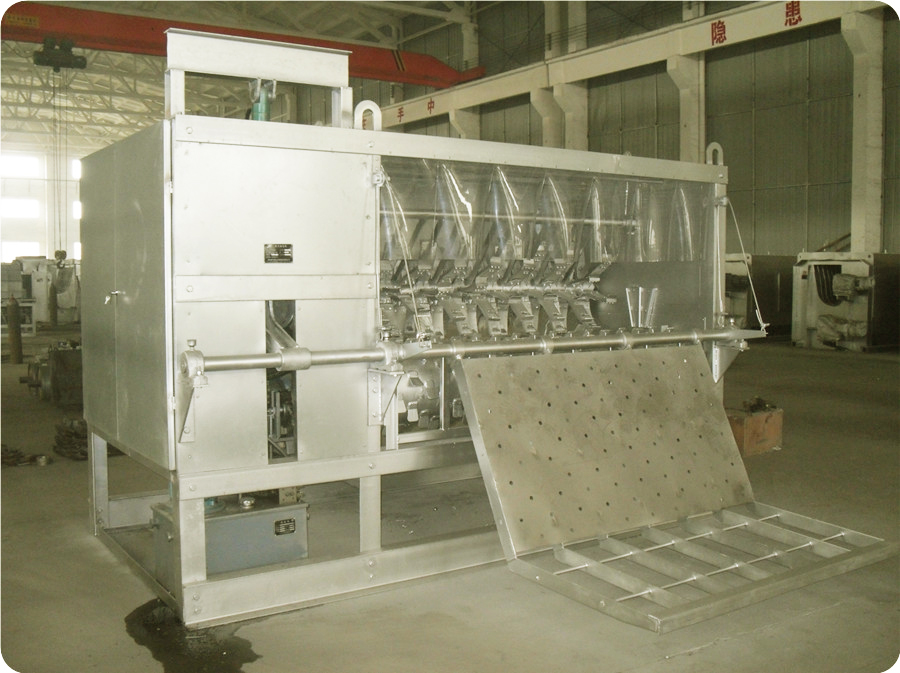
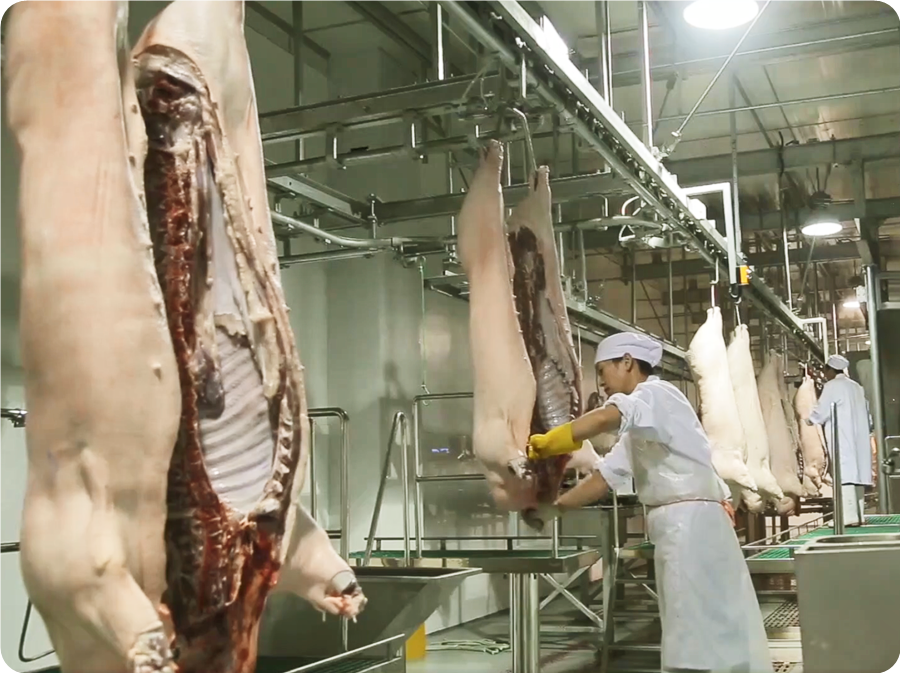
5.1. Carcass Processing Station: Carcass trimming, repair ear canal, rectal sealing, genital removal, thoracotomy, and sternal fracture, take white viscera, trichinella test, prefetch red viscera, take red viscera, split in half, inspection, remove suet, etc., are all completed on the automatic carcass processing conveyor line. The height of the track design from the workshop floor should be higher than 2400mm.
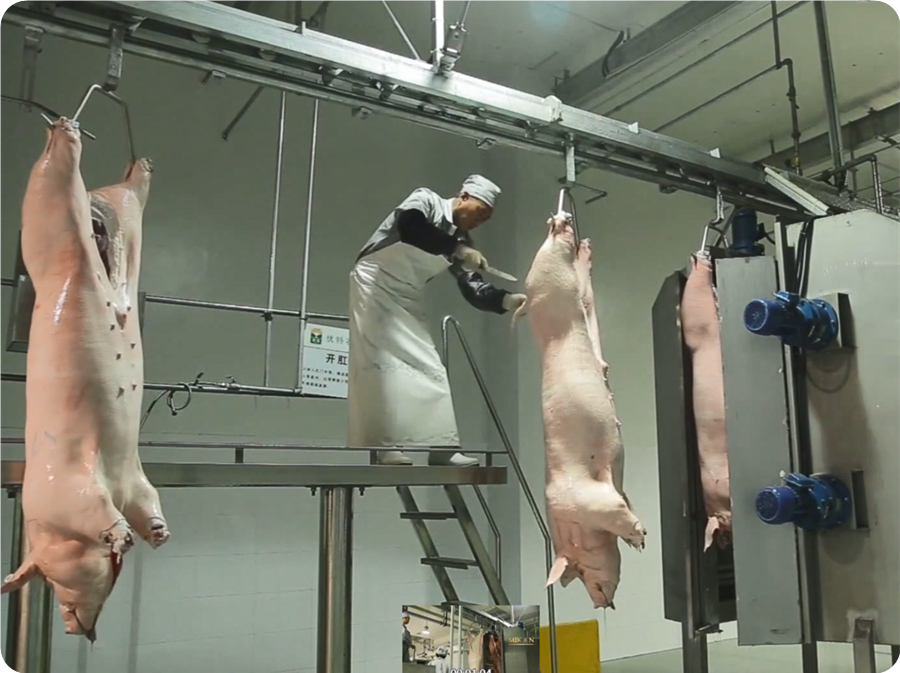

5.2. After opening the pig’s breast, remove the white viscera, namely the intestines and stomach, and put them into the tray of the white viscera quarantine conveyor for inspection. Take out the red viscera, namely the heart, liver, and lungs. And hang them on the hook of the red viscera synchronous quarantine conveyor for inspection.

5.3. Use a robot splitting half saw, belt splitting half saw, or a bridge splitting half saw to divide the pig into two halves evenly along the spine of the pig. A vertical accelerating machine should be installed directly above the bridge splitting half saw. Small slaughterhouses use reciprocating splitting and half sawing.

5.4. Cutting off the front hooves, back hooves, and pigtails. The hooves and tails are transported to the processing room for processing in a trolley.
5.5. Taking out of pork kidneys and removing suet, and transporting them to the processing room for processing.
5.6. The pig’s strips are trimmed, and then enter the orbital electronic scale for weighing. Grading and stamping are performed according to the weighing results.
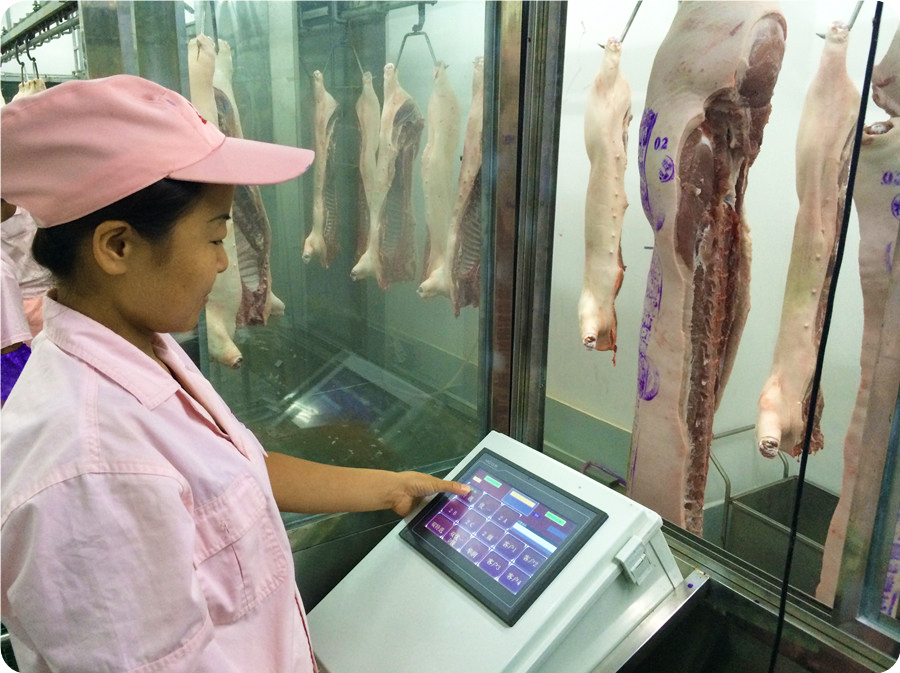

Step 6: Synchronous Sanitation Inspection
6.1. The pig carcass, white viscera, and red viscera are simultaneously transported to the inspection area through the quarantine conveyor for sampling and inspection.
6.2. Suspicious diseased carcasses shall enter the track through the switch for re-inspection. Make sure that the sick carcass enters the sick track line, and pull it out of the slaughterhouse with a closed cart for processing.
6.3. The unqualified white viscera shall be placed in a closed car and pulled out of the slaughterhouse for processing.
6.4. The unqualified red viscera shall be placed in a closed car and pulled out of the slaughterhouse for processing.
6.5. The red viscera hooks and white viscera trays on the synchronous health inspection line are automatically cleaned and disinfected by cold-hot-cold water.
Step 7: By-product Processing
7.1. The qualified white viscera enter the processing room through the chute. The contents in the stomach and intestine are poured into the air conveying tank and fill compressed air to transport through the air conveying pipe to about 50 meters away from the slaughterhouse. The stomach will be processed by a washing machine. Pack the cleaned intestines and stomach into cold storage or fresh-keeping warehouse.
7.2. Qualified red viscera enter the red viscera processing room through the chute. Cleaning the heart, liver, and lung, sort and package them into cold storage or fresh-keeping storage.
Step 8: Pig Strip Acid Excretion
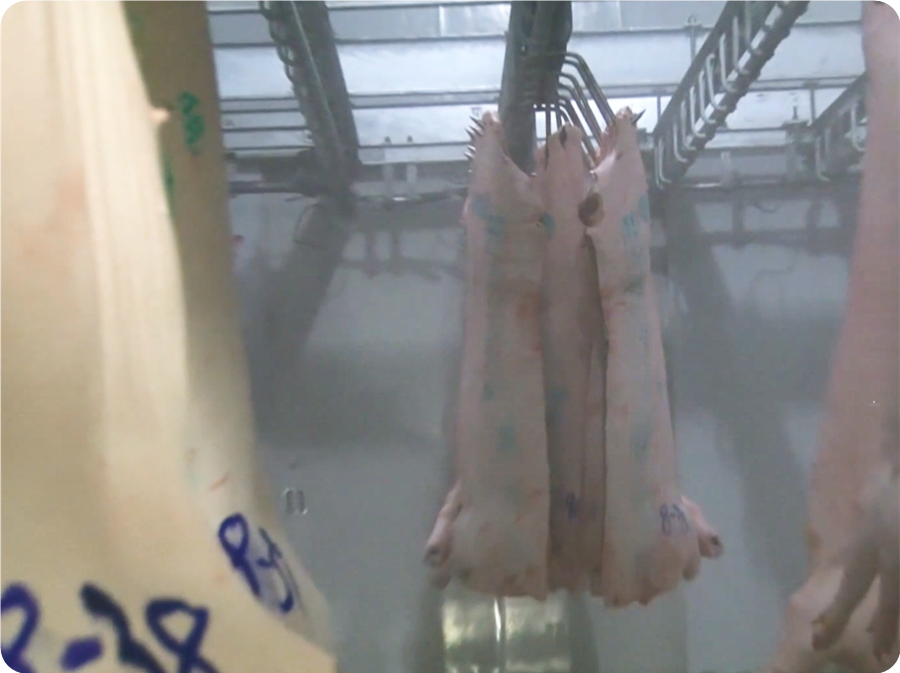
8.1. The trimmed and washed pig strip is put into the acid drainage room for “acid drainage”. This is an important link in the cold segmentation of mutton.

8.2. In order to shorten the acid excretion time, the rapid cooling process is designed. The temperature of the rapid cooling room is -20℃, and the time is 90 minutes.
8.3. Temperature of the acid excretion room is 0-4℃, and the time shall not exceed 16 hours.
8.4. The designed height of the acid excretion track from the floor of the acid discharge room is not less than 2400mm, and the track spacing is 800mm. 3 pig strips can be hung per meter of track.

Step 9: Cutting and Packaging
9.1. Unload the pig strips from the track, and divide each piece of pork into 3-4 sections with a segmented saw. Use a conveyor to automatically transfer them to the division staff’s station, then divide the meat into various parts.
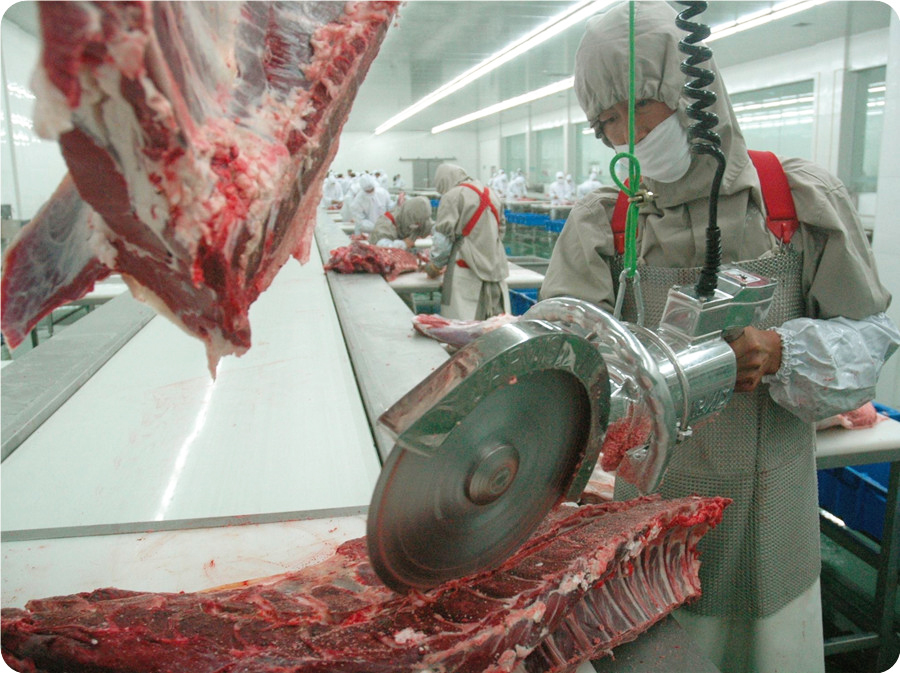
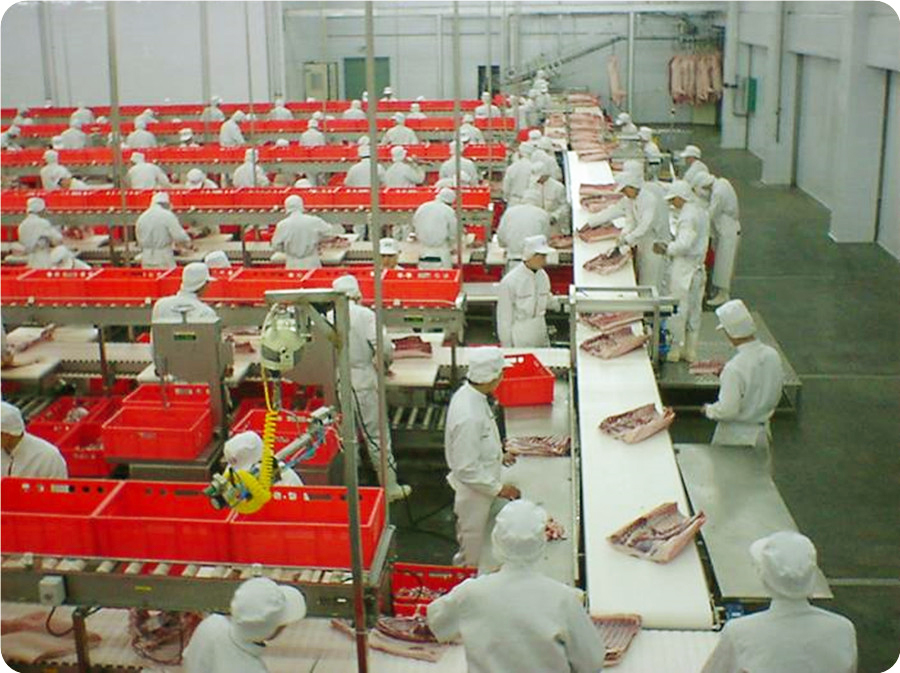


9.2 After the divided meat is vacuum packaged, it is put into the freezing tray and pushed to the freezing storage (-30℃) for freezing, or to the finished product cooling room (0-4℃) to keep it fresh.
9.3. Pack the frozen product and store them in the refrigerator (-18℃).
9.4 Temperature control of deboning and segmentation room: 10-15℃; Packaging room: below 10℃.








